.jpg)
- by Team Handson
- July 27, 2022
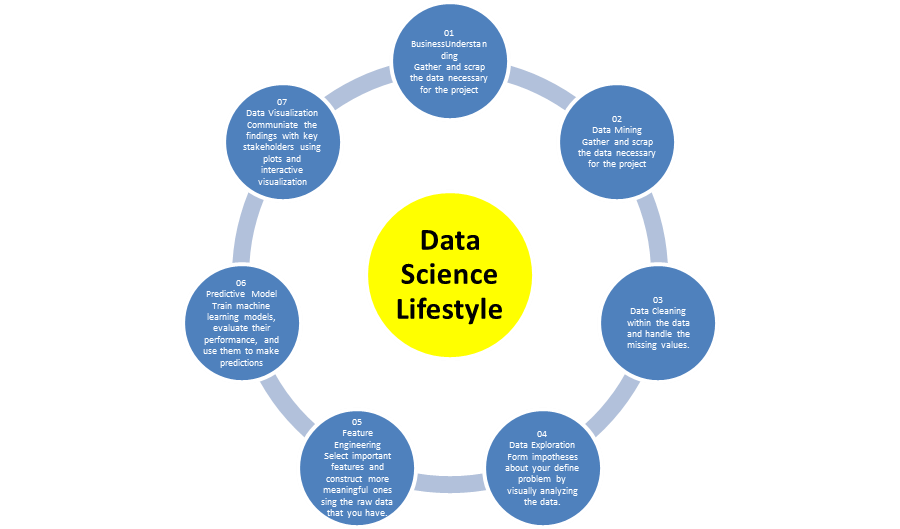
What is Data Science? Who are data scientist?
What is Data Science?
What is analytics? What is a data scientist?
“We have heaps of data – now what to do?”

(How can we find hidden value from our data?)
Value of your Business
Data science – finding of data insight
This feature of data science is all about revealing findings from data. Diving in at a rough level to mine and understand complex behaviours, trends, and inferences. It’s about surfacing hidden insight that can help allow companies to make smarter business decisions. For example:
- Netflix data mines movie performance patterns to understand what drives viewer interest, and uses that to make decisions on which Netflix original series to turn out.
- Fixing goal to target what are major customer segments and the unique users behaviours within those segments, which helps them to guide messaging to different target audiences.
- Proctor & Gamble using time series models to more clearly recognize future demand, which help plan for manufacture levels more optimally.
How do data scientists mine the insight of data? It starts with data investigation. When given a difficult issue, data scientists become detectives. They explore leads and try to understand pattern or features within the data. This requires a big amount of analytical methods.
Then as needed, data scientists may apply some technique like quantitative technique in order to get a level deeper – some examples are inferential models, segmentation analysis, time series forecasting, synthetic control experiments, etc. The aim is to scientifically bit together a forensic view of what the data is really saying.
This data-driven insight is core to providing strategic guidance. In this logic data scientists act as consultants, guiding business owners or decision makers on how to act on findings.
Data science – development of data product
We can say data product is a technical talent that: (1) utilizes data as input, and (2) processes that data to return algorithmically-generated results. The classic example of a data product is a recommendation engine, which ingests user data, and makes custom-made recommendations based on that data. Let us see some examples of data products:
- Amazon’s recommendation engines suggest products for you to purchase, single-minded by their algorithms. Netflix recommends movies to you. Spotify recommends composition to you.
- Gmail’s spam filter is data product – an algorithm behind the scenes processes incoming mail and determines if a message is scrap or not.
- Self-driving cars is also a data product – machine learning algorithms are capable to recognize traffic lights, other cars on the road, pedestrians, etc.
This is different from the “data insights” section mentioned above; where the result to that is to perhaps provide advice to an executive to make a smarter decision. Alternatively, a data product is technical functionality that encapsulates an algorithm, and is designed to integrate directly into core applications. Individual examples of applications that have as a feature data product behind the scenes: Amazon’s homepage, Gmail’s inbox, and autonomous driving software.
Data scientists play a core role in developing data product. Data scientists are building out algorithms, as well as testing, refinement, and technical use into production systems. In this logic, data scientists serve as technical developers, building assets that can be leveraged at wide scale.